FWF P35241 - The Neolignan-derived Rexinoid LRK071
| Project title: | The Neolignan-derived Rexinoid LRK071. |
| Project number: | FWF stand alone project P35241 |
| Project leader: | Dr. Verena M. Dirsch verena.dirsch@univie.ac.at |
| Duration: | 2022 - 2026 |
| Location: | University of Vienna, Faculty of Life Sciences Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences Althanstraße 14, 1090 Vienna, Austria |
Background
Nuclear receptors are intracellular ligand-binding transcription factors allowing ligand-dependent transcriptional regulation.1 Type II nuclear receptors act as heterodimers, in which one partner is the retinoid X receptor (RXR). Heterodimers that are classified as “permissive” can be activated next to the ligands for the partner receptor also by rexinoids (ligands for RXR). Nuclear receptors that are cooperatively regulated by RXR act mainly as metabolic sensors and are thus interesting targets for the treatment of metabolic disease.2 Direct activation of these nuclear receptors (e.g. LXRs or PPARs) by strong agonists may, however, have side effects, such as lipid accumulation in the liver or adipose tissue.3 So-called selective RXR modulators (SRXRM) that act tissue-selective or as hetero- and homodimer-specific agonists or antagonists may have therapeutic potential for metabolic disease without severe side effects.4,5
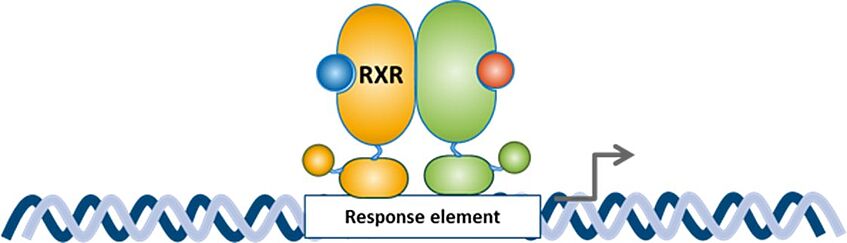
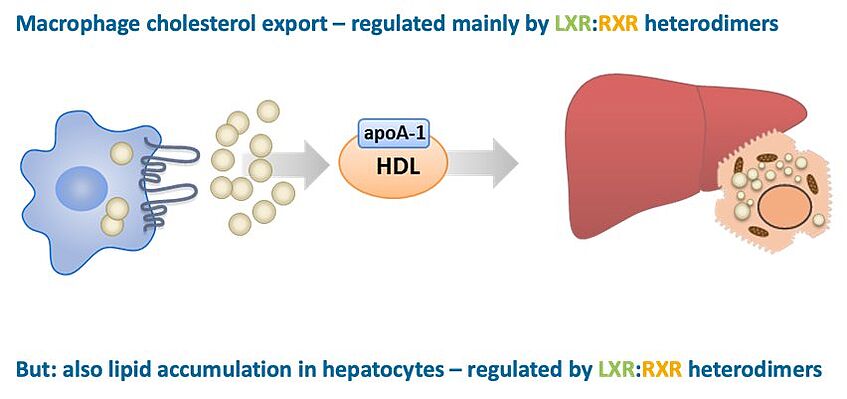
Based on a screening initiative of a previous FWF-project (NFN: S10704-B13) we identified a neolignane analog as partial RXR agonist with superior properties as the parent natural product.
Aim
… will be to characterize the rexinoid in more detail in vitro, to use it as tool compound to create mechanistic knowledge gain, and to obtain first in vitro and in vivo data regarding a potential “druggability”.
Objectives
...will answer the following questions:
- Does the rexinoid act heterodimer-selective and/or cell-type specific?
- Can a heterodimer selectivity be linked to a specific structural change in the RXRα-LBD?
- How does the rexinoid change the gene expression and lipid profile in functional cell models and in tissue?
- How do specific cellular functions observed for the rexinoid occur? (mechanistic studies)
People
- Verena M. Dirsch; Principal investigator
- Mirta Resetar; graduate student
References
- 1Glass CK, Ogawa S. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:44-55, 2006.
- 2Evans RM, Mangelsdorf DJ. Cell. 157:255-66, 2014.
- 3Fessler MB. Pharmacol Ther. 181:1-12, 2018.
- 4Gilardi F, Desvergne B. Subcell Biochem. 70:75-102, 2014.
- 5Hiebl V, Ladurner A, Latkolik S, Dirsch VM. Biotechnol Adv. pii: S0734-9750(18)30041-7, 2018.
